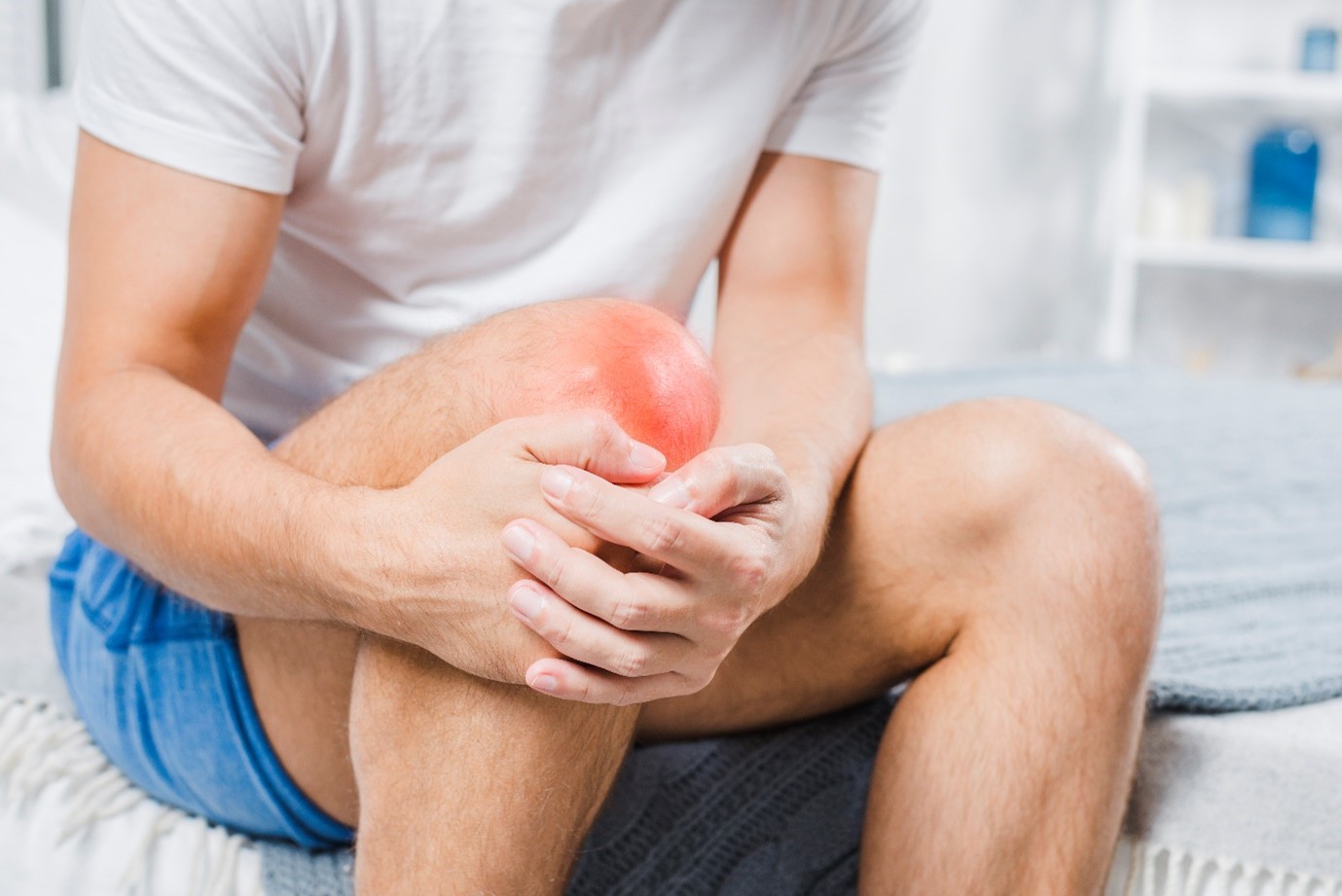
Knee osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint condition that causes pain, stiffness, and limited mobility.
Symptoms:
- Persistent knee discomfort is made worse by weight-bearing activities.
- Morning stiffness and decreased range of motion.
- Swelling, warmth, and discomfort at the knee joint.
- Crepitus is a grinding sensation that occurs when moving.
- It is difficult to fully bend or straighten the knee.
Causes and Risk Factors:
- Joint tissues deteriorate with age.
- Obesity causes increased stress on the knees.
- Previous knee injury or surgery.
- Genetic tendency to osteoarthritis.
- Overuse or repeated stress on the knees.
Lifestyle Changes: Maintain a healthy weight through food and exercise to relieve knee pressure. Low-impact sports such as swimming or cycling can help to increase joint flexibility and strength.
Physical therapy: Perform focused exercises to strengthen the knee-supporting muscles and increase range of motion. Physical therapists can help you develop individualized workout programs.
Medications: Acetaminophen and other over-the-counter pain medicines, such as NSAIDs, can help with pain and inflammation. Corticosteroid injections can give short relief from severe pain.
Assistive devices: Supportive braces, orthotic shoe inserts, and canes can all assist in minimising joint stress and increase mobility, particularly during weight-bearing tasks.
For severe instances that do not respond to conservative therapies, consider surgical alternatives such as arthroscopic debridement, partial knee replacement, or total knee replacement.